The AI Traffic module in SEO Booster Pro reveals how AI/LLM systems interact with your website. It detects visits from AI model crawlers, AI search indexers, and real‑time assistant fetchers, then organizes those visits into clear charts and actionable reports.
By understanding which AI systems read your pages, and how often, you can prioritize content improvements, fix technical issues that waste crawl budget, and align your site with the evolving AI search landscape.
Contents
Key facts
- Data privacy: All AI Traffic detection and storage happen locally on your website. AI Traffic data never leaves your server.
- Data freshness: Real time. Visits are recorded as they happen.
- Retention: Last 30 days of AI bot activity are kept.
- GSC comparison: If your site is connected to Google Search Console, the module will display available per‑URL GSC metrics automatically.
- Bot coverage: We maintain a growing list of recognized AI bots. If you notice one missing, you’re welcome to submit it.
Bot categories we track
- Bulk Crawlers
Systematic crawlers that collect content for training AI models (e.g., Common Crawl, AI2Bot). Spikes typically indicate ingestion windows rather than direct user demand.
- Why it matters: Understand when your content is being ingested into model corpora.
- What to do: Ensure accuracy, resolve errors, and review crawler access policies if needed.
- Search Indexers
Crawlers used by AI‑powered search engines (e.g., Bingbot, Googlebot) to build indices. Activity mirrors traditional SEO signals but increasingly affects AI search experiences.
- Why it matters: Consistent indexing and clean signals help your content surface in AI‑powered search results.
- What to do: Strengthen structured data (FAQ, HowTo, Article), improve internal links and page speed, minimize unnecessary redirects.
- On‑Demand Fetchers
Real‑time requests triggered when users ask questions in AI assistants (e.g., ChatGPT, Claude). These are most likely to correlate with real user visibility and potential referral traffic.
- Why it matters: Pages fetched by assistants are already being checked or cited in live user sessions.
- What to do: Tighten summaries and intros, add FAQs, keep facts and prices updated, surface clear CTAs, ensure fast load and mobile readiness.
Where you’ll see AI Traffic
A) Overview dashboard widget (on the main SEO Booster overview page)
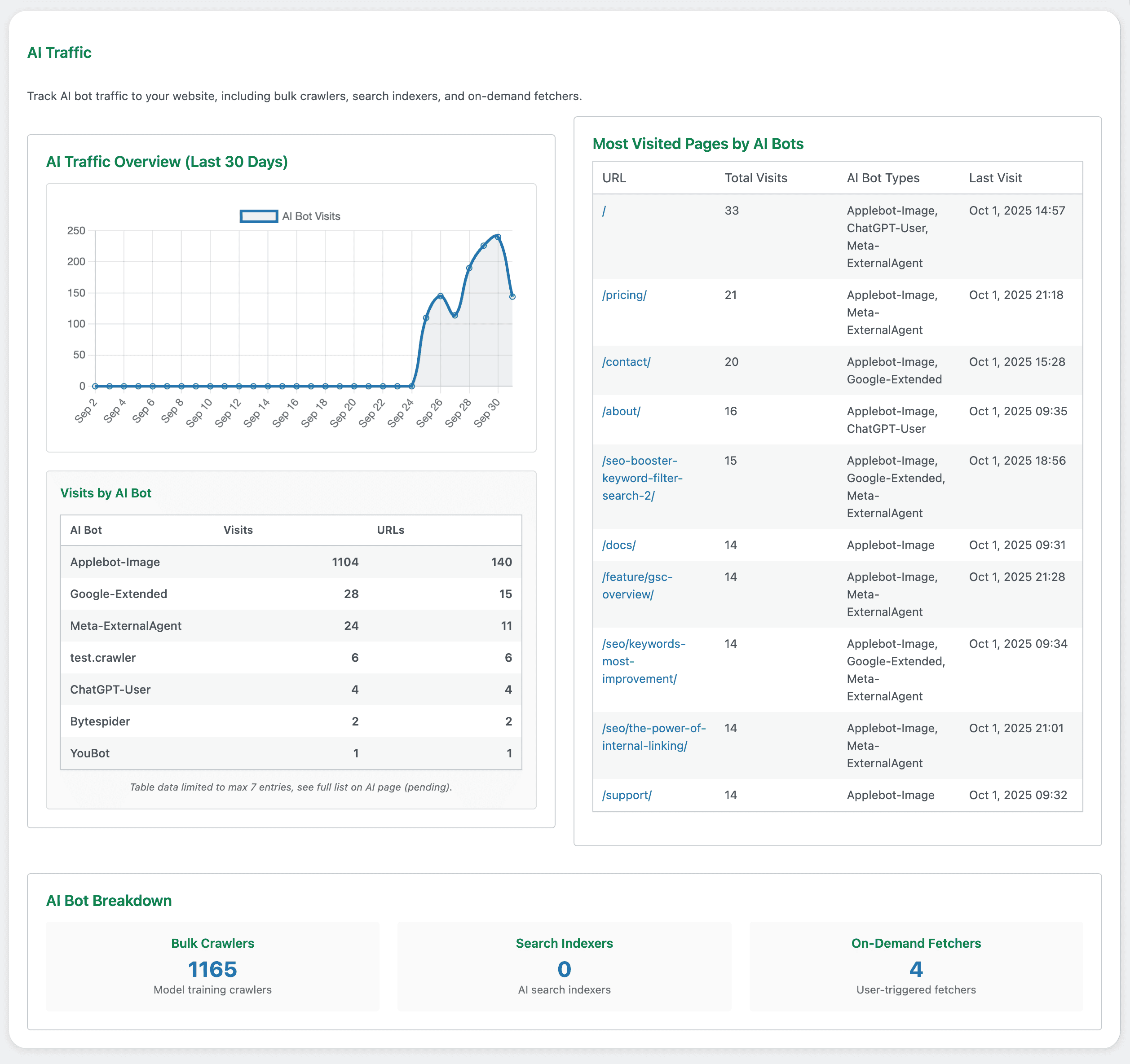
- AI Traffic Overview (Last 30 Days): A line chart of total AI bot visits over the past 30 days. You can quickly spot surges or dips.
- Visits by AI Bot: A ranked table of the most active AI bots, showing total visits and the count of distinct URLs they accessed. This helps you see which bots dominate your crawl mix.
- Most Visited Pages by AI Bots: A list of URLs getting the most AI visits, with columns for total visits, the AI bot types that visited, and the last visit time. Use this to find content that AI systems repeatedly check.
- AI Bot Breakdown: Summary tiles tallying visits by category—Bulk Crawlers, Search Indexers, and On‑Demand Fetchers—so you grasp your overall exposure at a glance.
What counts as a “visit”?
Each AI bot request recorded and attributed to a recognized AI/LLM crawler or fetcher within the last 30 days.
B) Admin > AI Traffic (full report)
This page expands on the overview, offering deeper analysis and practical filtering.
-
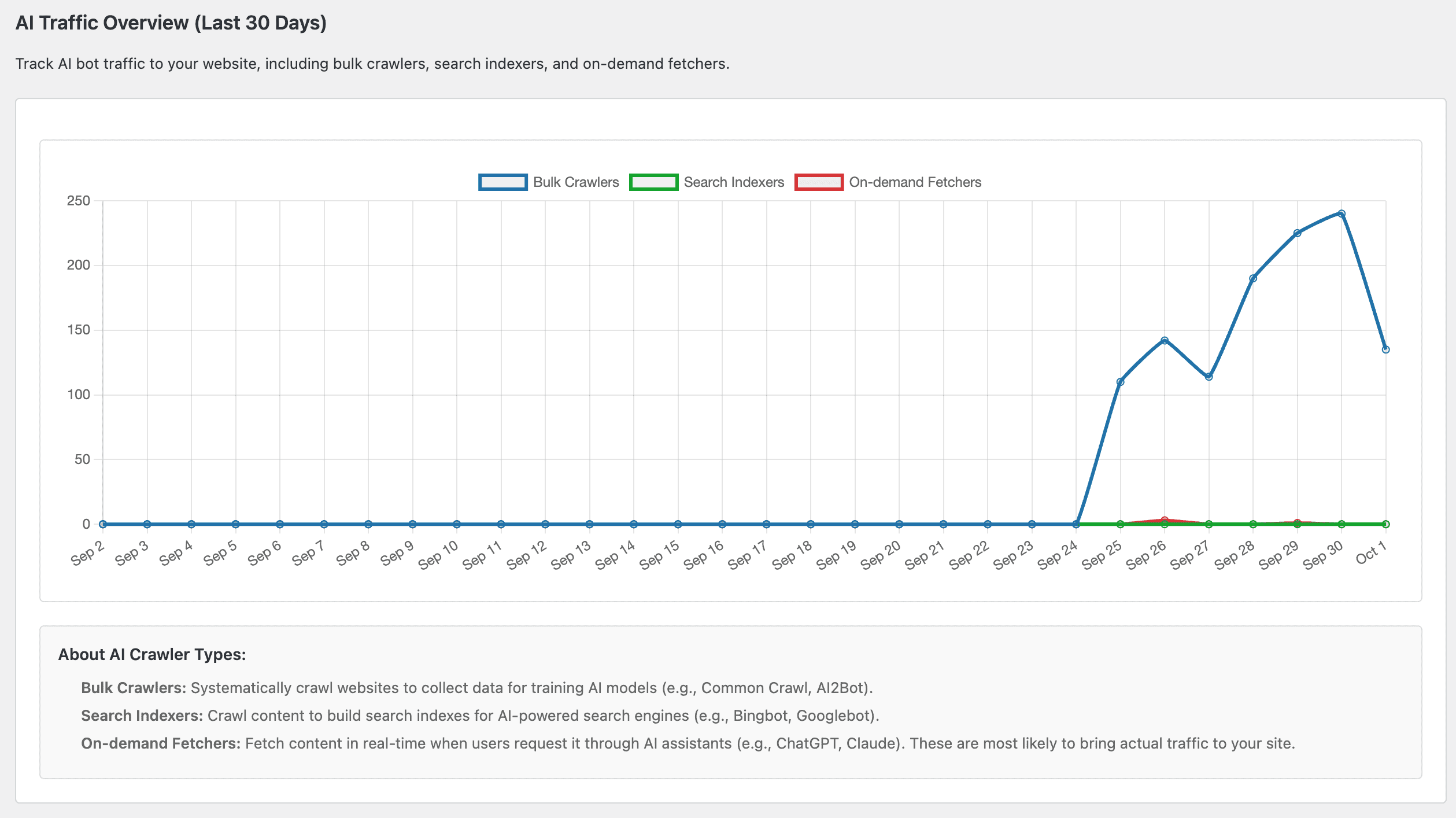
AI Traffic Overview (Last 30 Days) chart with three series:
- Bulk Crawlers
- Search Indexers
- On‑Demand Fetchers
Use this to spot model‑training surges, increases in AI search indexing, and growing assistant‑driven interest. Changes in the mix often hint at evolving distribution across models and search surfaces.
-
About AI Crawler Types
A short explainer of the three classes so teams share a common vocabulary and can interpret trends consistently. -
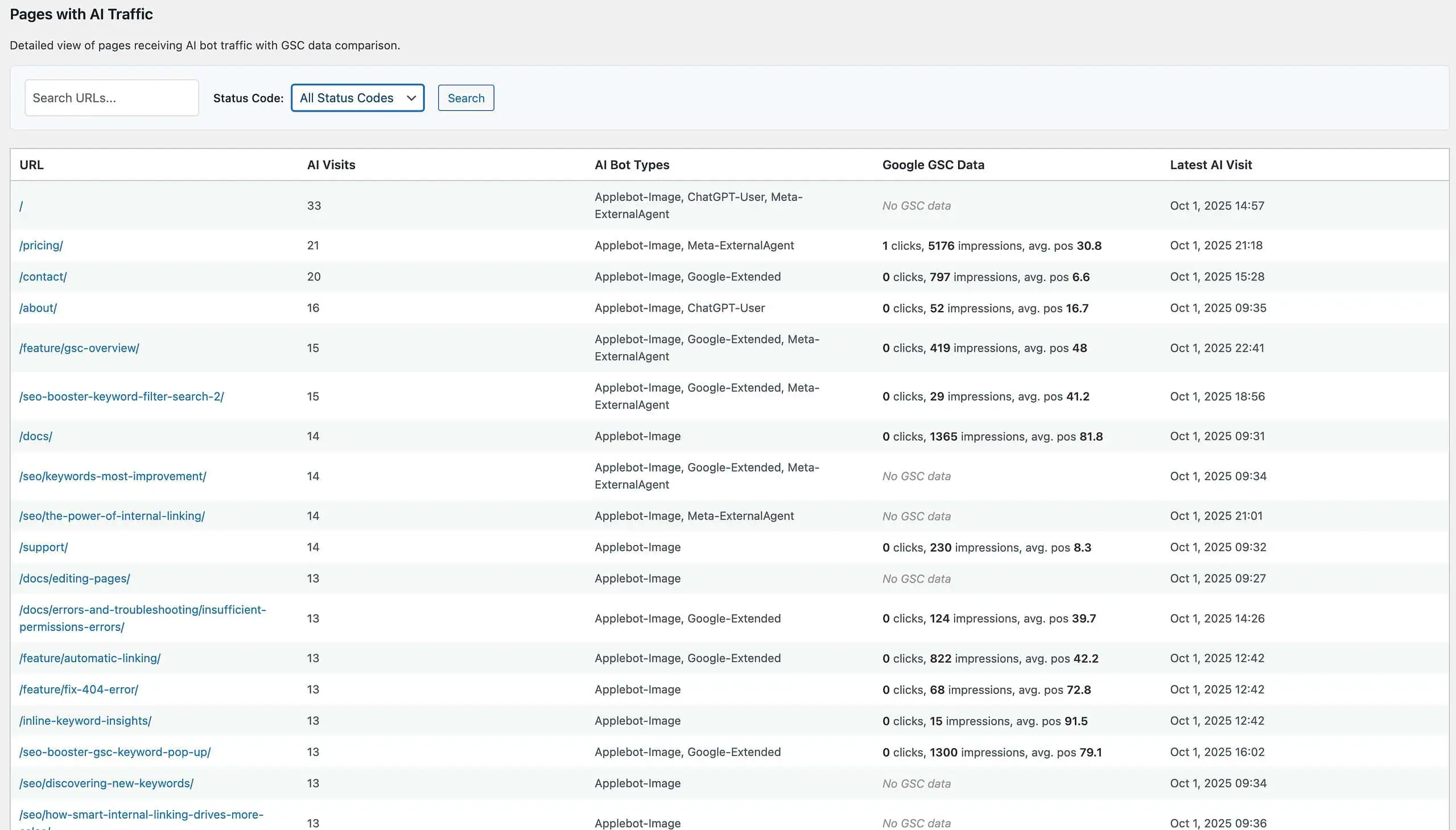
Pages with AI Traffic
A detailed table of URLs that received AI visits, with:- AI Visits (past 30 days)
- AI Bot Types (one or more labels per URL)
- Google GSC Data (if available): clicks, impressions, average position
- Latest AI Visit (timestamp)
Tools for working the list: - Status code filter: All, 2xx, 3xx, 4xx+, 5xx+
- URL search: Quickly find specific pages or diagnose a path
GSC comparison notes: - The AI Traffic module automatically surfaces GSC metrics for connected sites. It’s normal for AI visits to differ from GSC clicks/impressions; GSC reflects Google Search user behavior, while AI visits reflect AI bots and assistant fetches.

How to use the insights
Content strategy
- Prioritize pages with frequent On‑Demand Fetcher hits. These pages are being checked during live assistant interactions—improve clarity, accuracy, and conversion paths.
- For pages frequently visited by Search Indexers, enrich structured data (FAQ, HowTo, Product, Article), tighten headings, and ensure your key points are easy to extract.
Technical SEO
- Use status code filters to find AI‑visited pages returning 3xx/4xx/5xx. Fix broken links, reduce redirect chains, and investigate server errors to avoid wasting crawl and missing assistant citations.
- Validate canonical tags and internal links on AI‑trafficked hubs to consolidate signals and improve discoverability of deeper content.
Brand and compliance
- Bulk Crawler trends show when and how model training sources ingest your content. Use this signal to review your content accuracy, disclosure policies, and crawler access preferences.
Capacity planning
- If you see recurring Bulk Crawler surges, consider server resource planning and cache strategies to handle load without impacting user experience.
Practical workflows
- Find high assistant attention pages
- In “Pages with AI Traffic,” sort by AI Visits and scan for URLs with On‑Demand Fetchers in AI Bot Types.
- Actions: Refresh summaries/FAQs, ensure fast load, add internal links to related conversions.
- Fix high‑impact errors quickly
- Filter Status Code to 4xx+ or 5xx+ and sort by AI Visits.
- Actions: Resolve 404s and server errors where AI bots are active; these errors can reduce how often assistants and AI search rely on your content.
- Bridge AI activity and SEO outcomes
- Compare AI Visits vs. GSC metrics for the same URLs.
- Actions: If AI activity is high but GSC clicks/impressions are low, consider richer schema, improved titles/meta, and better internal linking.
- Prepare for ingestion windows
- Watch Bulk Crawler spikes on the 30‑day chart.
- Actions: During spikes, ensure key pages are accurate and current. Consider how summaries, tables, and FAQ blocks present your facts.
FAQs
How fresh is the data?
Real time. Visits are recorded as they happen and stored locally on your site.
How long is AI traffic kept?
The last 30 days.
Do I need to do anything to see GSC data?
No special setup here. If your site is already connected to Google Search Console in SEO Booster Pro, we’ll display per‑URL GSC metrics when available.
Why does a page have AI visits but “No GSC data”?
That URL might not have recent GSC metrics, or it isn’t covered in GSC’s current reporting. AI visits reflect bot activity; GSC reflects Google Search user interactions.
How are bots identified?
Through known bot signatures and heuristics. Our list is growing—please submit AI bots you think are missing so we can evaluate and add them.
Can I export AI Traffic data?
Not yet.
Does any AI Traffic data leave my site?
No. All detection and storage are local to your website.